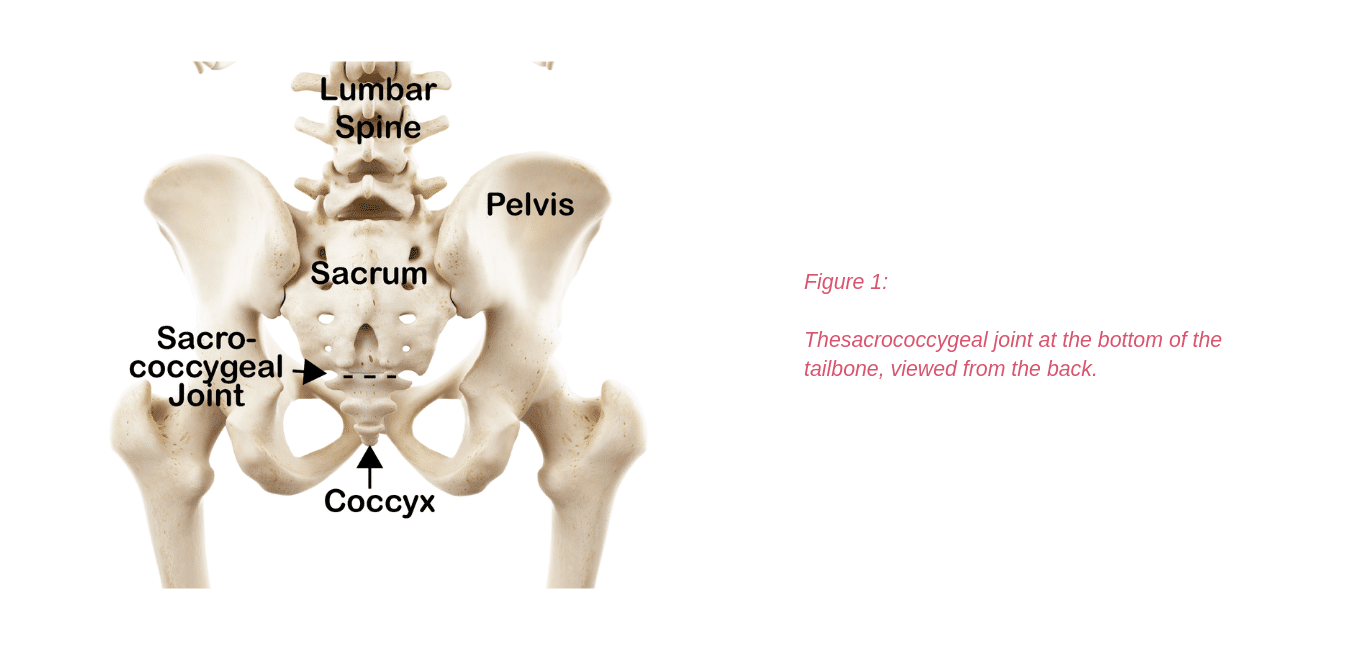
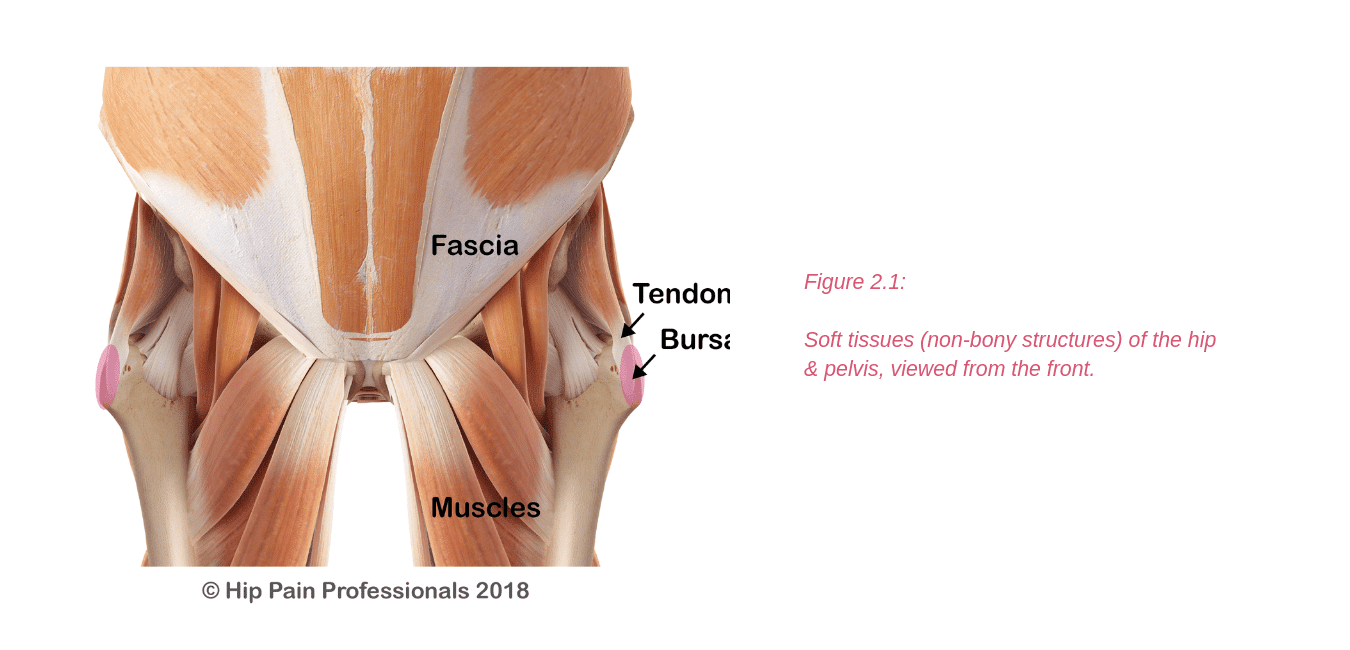
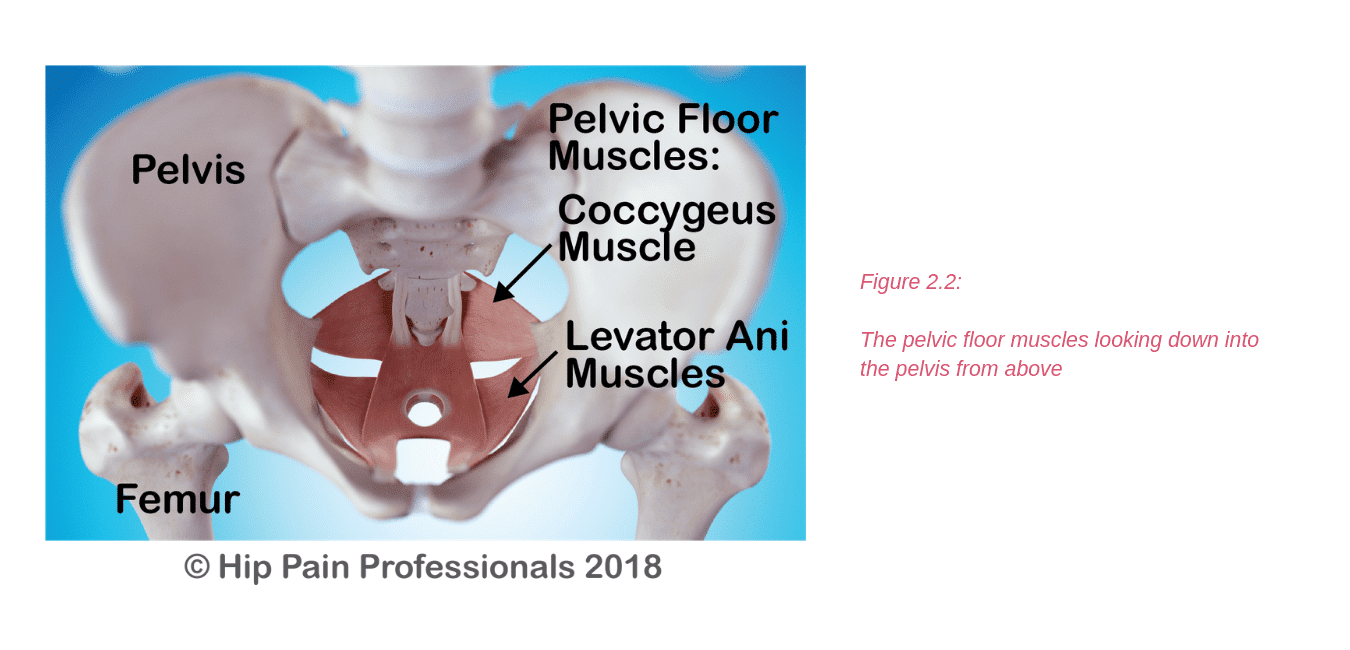
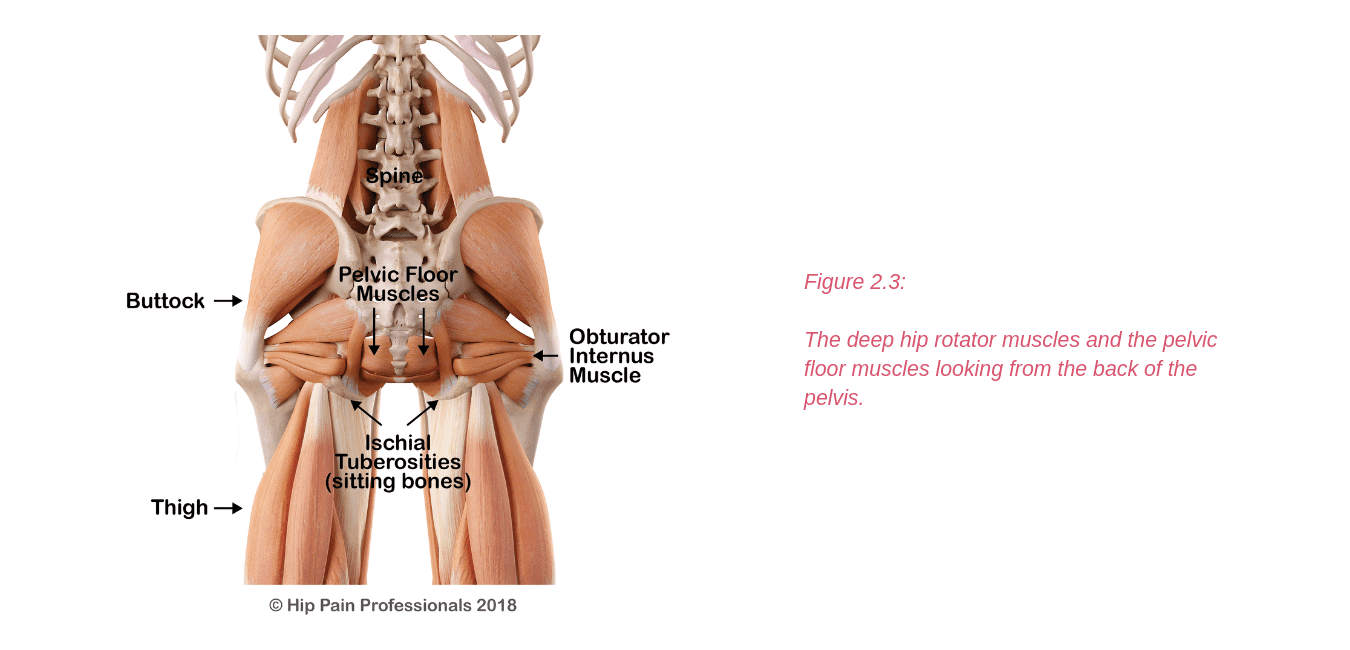
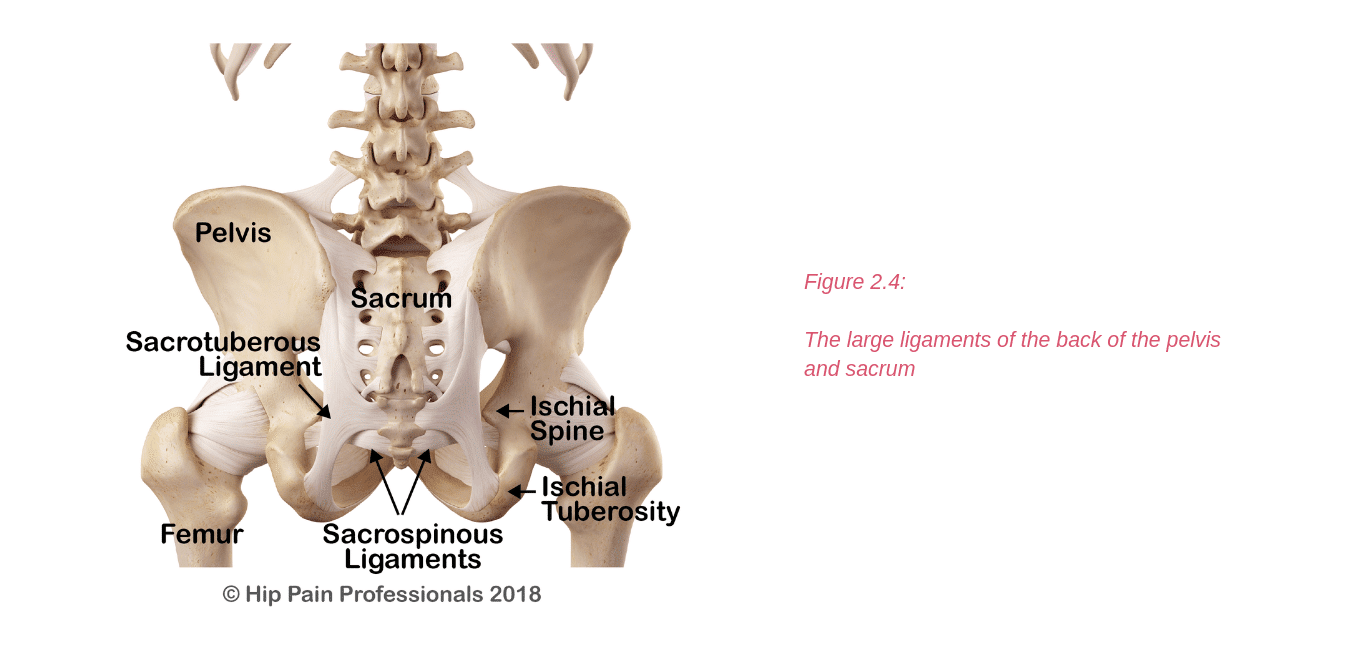
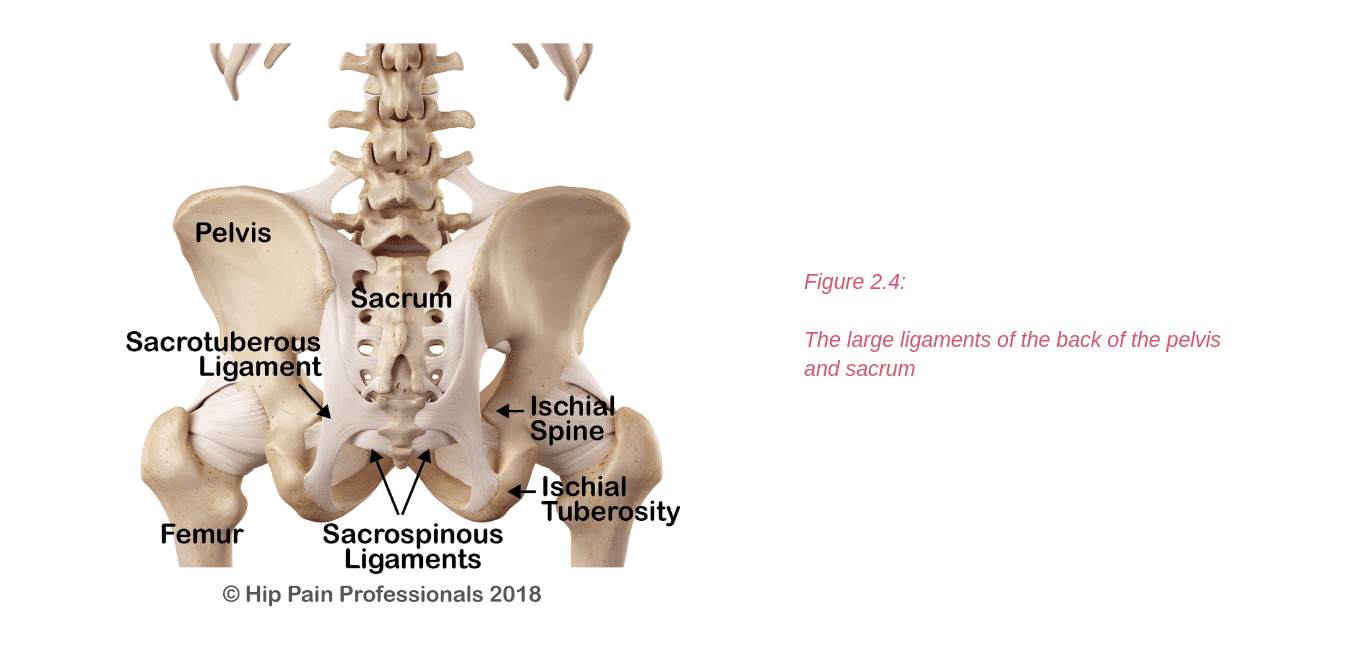
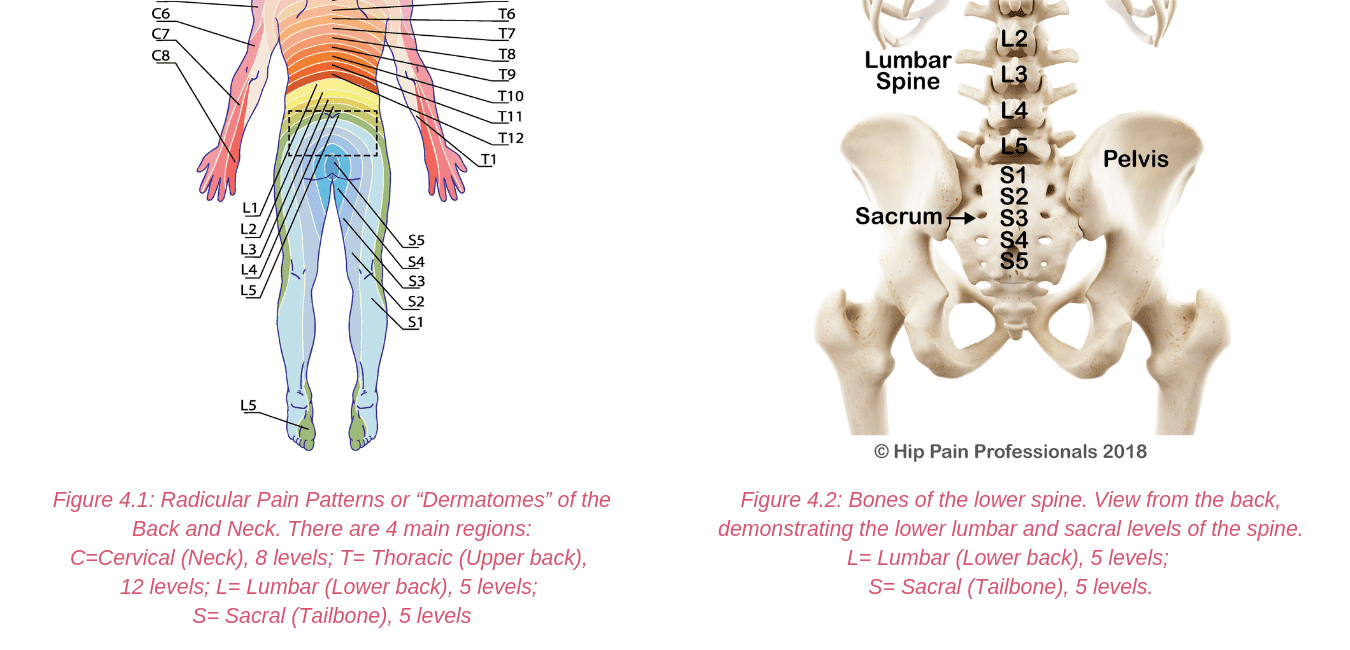
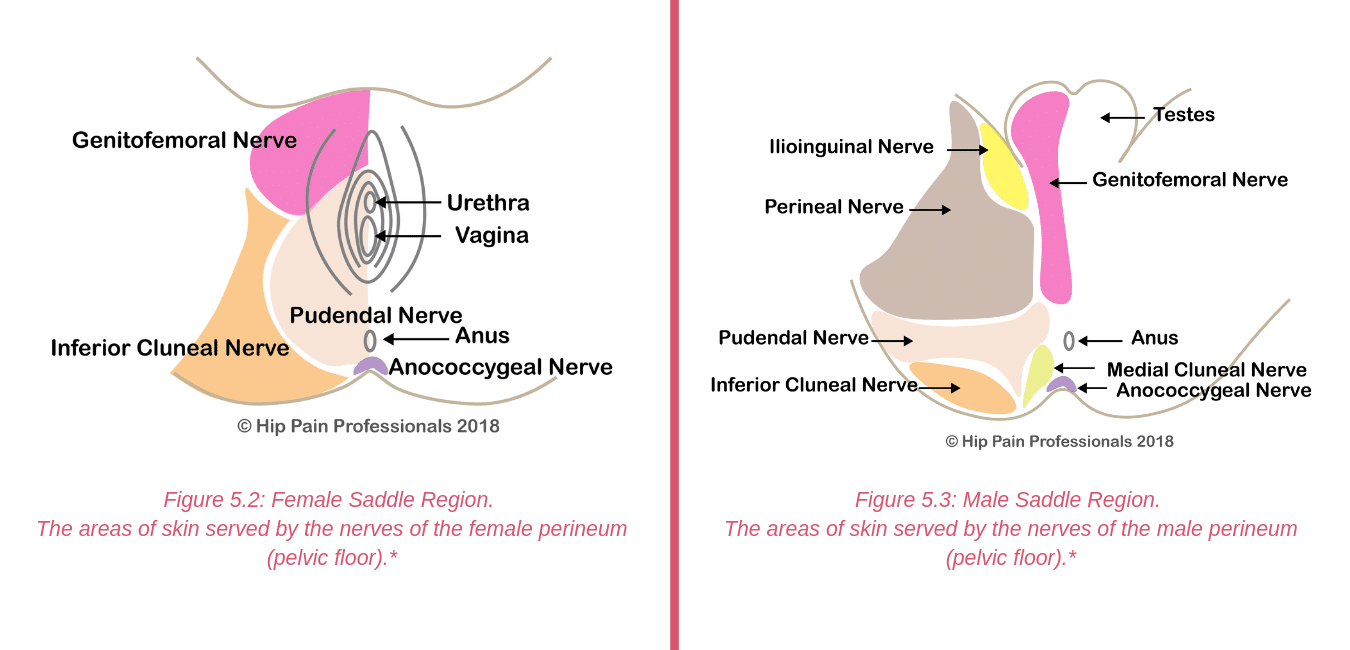
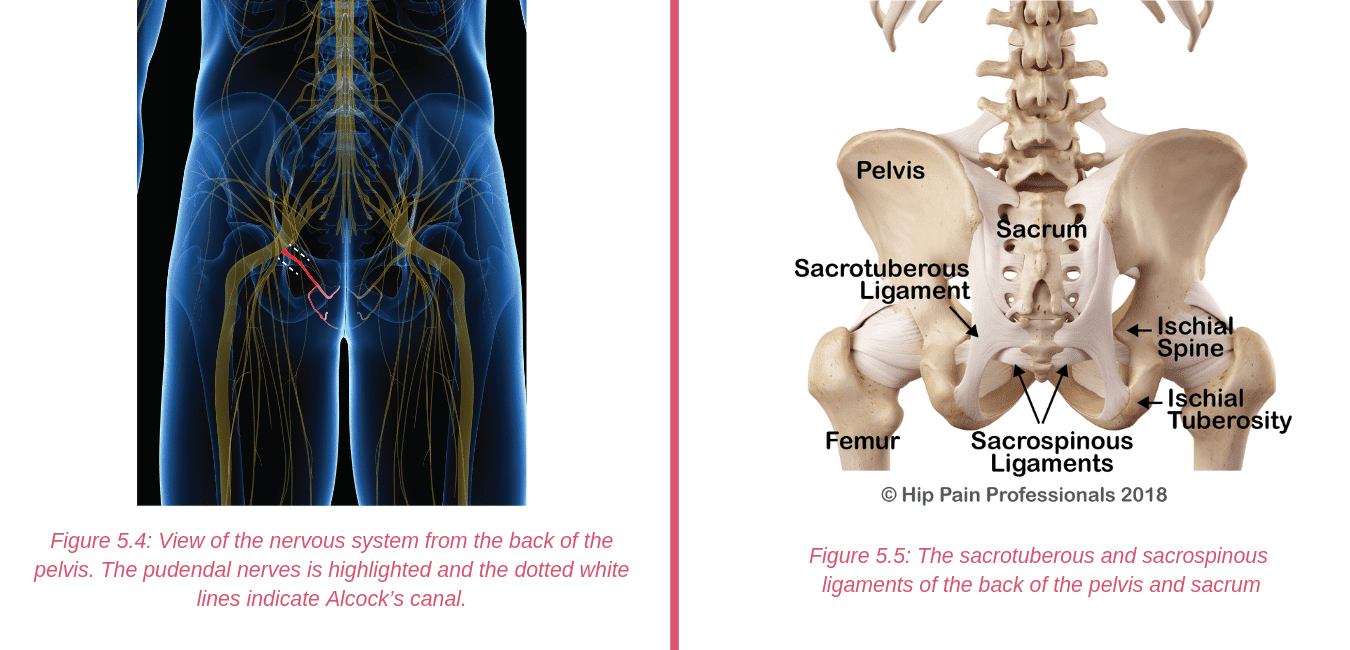
There are other processes that may produce pain around the hip and pelvis.
These include:
- Systemic/Rheumatological conditions: eg Rheumatoid Arthritis, Polymyalgia, Polyarthralgia
- Infective processes: Septic arthritis, Osteomyelitis, Viral Arthritis
- Neoplastic processes (cancer)
- Vascular issues: Avascular Necrosis, External Iliac Artery Entrapment, varicotic gluteal vessels compressing the sciatic nerve
These conditions are relatively rare compared to musculoskeletal pain, but when present you will need to see a medical practitioner and usually a specialist for that system or problem, for example, a Rheumatologist, Orthopaedic Specialist, Oncologistor Vascular Specialist.
Lower abdominal and pelvic pain can also be associated with organ problems (ovaries, uterus, bowel, bladder, prostate). One of the most common causes of organ-related pain in females is endometriosis.
This occurs when tissue that is similar to the lining of the uterus (womb) grows outside the uterus attaching to other structures such as the pelvic ligaments or the bladder and bowel.
This can lead to debilitating pain that may be cyclic, relating to the menstrual cycle.
Diagnosis and management of organ related problems will usually require the assistance of a specialist, for example a gynaecologist (female reproductive organs), urologist (bladder and prostate) or gastroenterologist (gut/bowel).
A skilled assessment by a Hip Pain Professional will help clarify if the problem requires further medical attention and whether it is likely to be related to a musculoskeletal problem or not.
- provide a detailed assessment
- assist in determining if the problem is musculoskeletal or not
- develop a plan to help if the problem is musculoskeletal
- recommend further tests or send you to another specialist if the problem does not appear to be in the musculoskeletal system.


 Joint Related
Joint Related  Soft Tissue Related
Soft Tissue Related  Bone Related
Bone Related  Back Related
Back Related  Peripheral Nerve
Peripheral Nerve  Other causes
Other causes